|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
The financial landscape is shaped by central banks’ interest rate decisions, directly impacting how banks structure their loan offerings. Whether central banks tighten or loosen monetary policy, commercial banks adjust their lending strategies accordingly, offering fixed or variable-rate loans based on prevailing trends. Understanding this correlation is crucial for borrowers, businesses, and policymakers navigating economic cycles.
Central Banks’ Role in Setting Interest Rate Trends
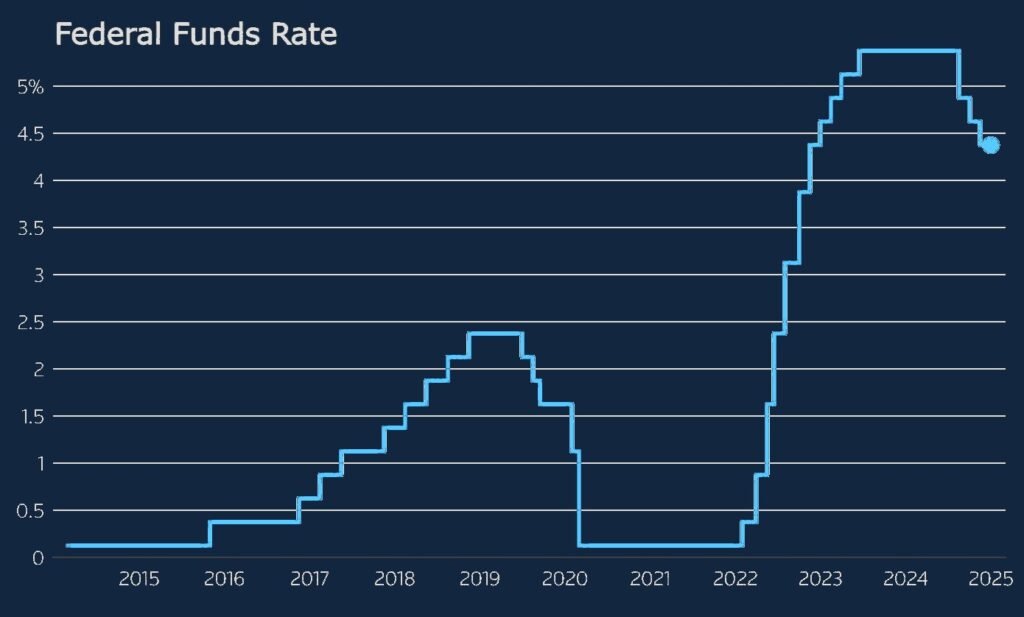
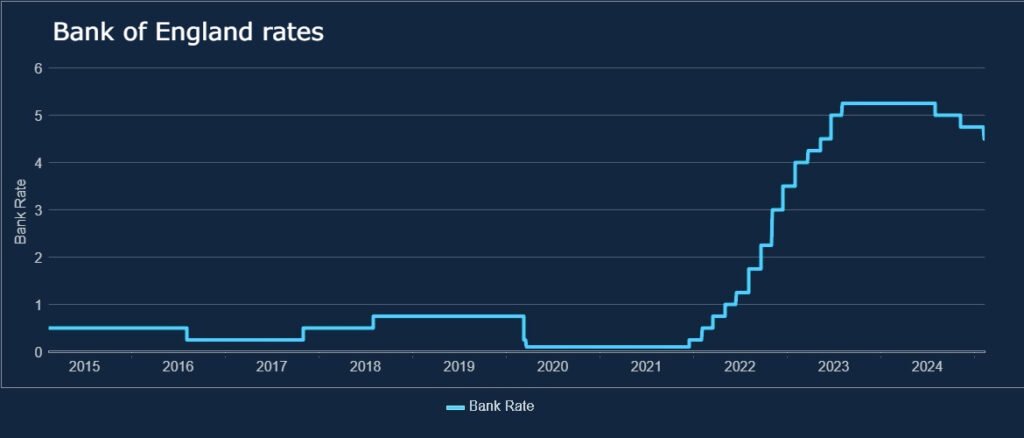
Central banks such as the Federal Reserve (U.S.), the European Central Bank (ECB), and the Bank of England influence borrowing costs by setting benchmark rates. These rates determine the cost of funds for banks, impacting the interest rates offered on loans and credit products. Recent trends indicate that central banks in advanced and emerging economies have shifted policies significantly, either hiking rates to combat inflation or cutting rates to stimulate economic activity.
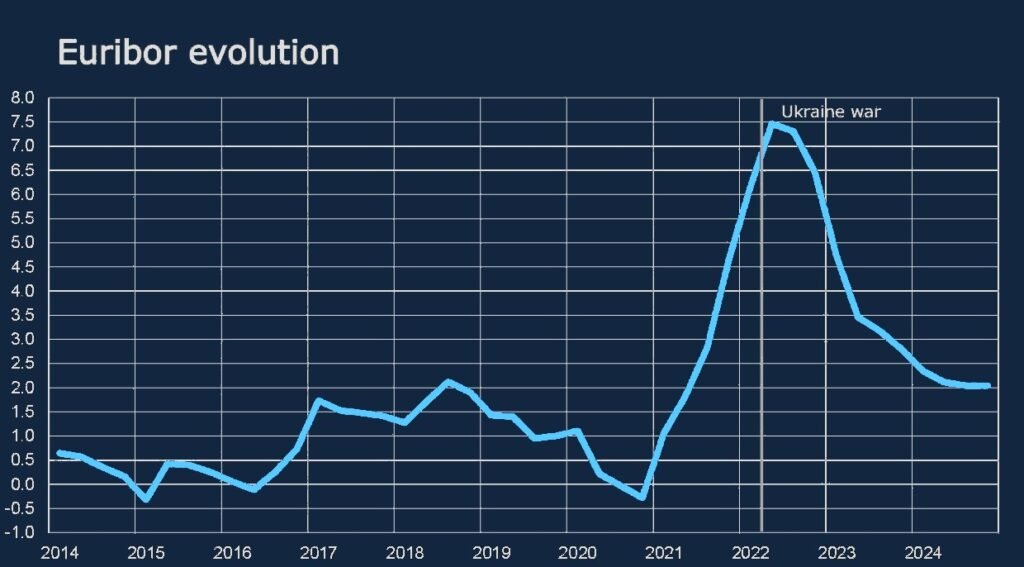
According to Statista, global central bank policy rates have diverged significantly. While advanced economies like the U.S. and the Eurozone experienced rate hikes between 2022 and 2023, emerging markets saw more flexibility, with some central banks easing rates earlier to support economic growth. The European Central Bank data reveals a strong correlation between these changes and shifts in bank lending rates.
How do Interest Rate Trends Influence Loan Offers?
The type of loan banks offer—fixed-rate or variable-rate—depends largely on their analysts’ expectations regarding central bank rate movements.
- Fixed-Rate Loans: When central bank analysts predict a downward trend in interest rates, banks are more likely to offer fixed-rate loans at competitive rates. This allows borrowers to lock in a stable interest rate before further declines, providing long-term security in an environment where rates may eventually bottom out.
- Variable-Rate Loans: In contrast, when central banks are on a tightening cycle, banks introduce more variable-rate loans. This structure allows financial institutions to adjust loan rates upward in response to increasing central bank rates, ensuring profitability in a rising-rate environment.
The Current Trend: Are Rates Heading Up or Down?
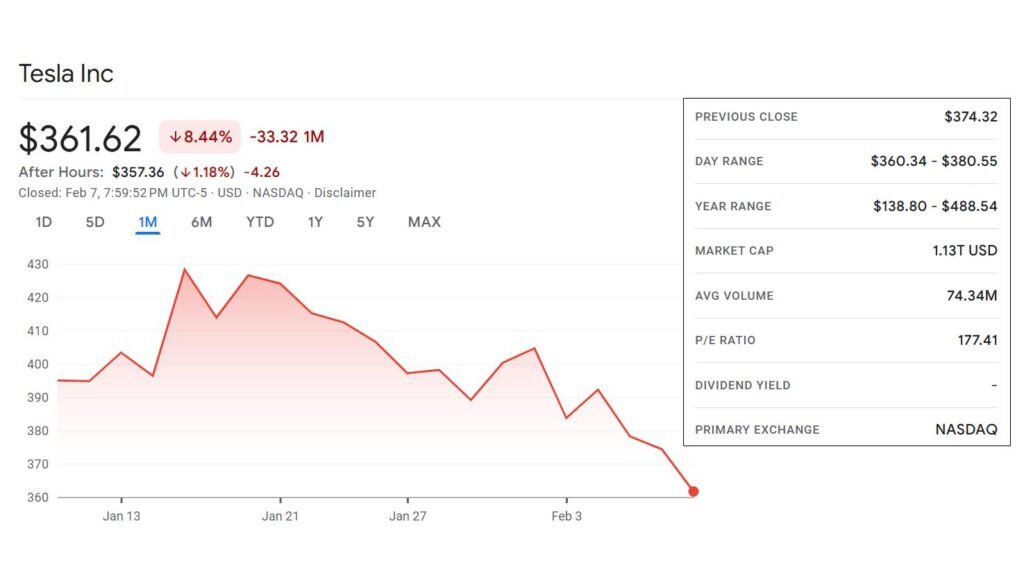
As per OANDA’s latest analysis, a growing number of central banks are transitioning toward lower interest rates following aggressive hikes in 2022-2023. This shift signals a move toward fixed-rate loan offers by commercial banks, as they seek to lock in borrowers at current levels before further declines. However, in regions where inflation remains persistent, such as the U.K. and parts of the U.S., banks still lean towards variable-rate loans, anticipating prolonged rate hikes.
The ECB’s loan interest rate data confirms that euro-area banks are already adjusting mortgage and business lending rates downward, anticipating future cuts in central rates. Meanwhile, U.S. mortgage lenders still favor variable-rate structures as the Federal Reserve remains cautious about inflation trends.
Strategic Banking Adjustments in Response to Interest Rate Trends
Banks must remain agile, aligning their lending products with market expectations. A high-rate environment leads to more restrictive credit conditions, prompting banks to be selective with loan approvals. Conversely, when central banks signal rate cuts, banks ease lending conditions to attract borrowers before interest rates decline further.
In practical terms, this means that homebuyers, corporate borrowers, and small businesses should closely monitor central bank signals when choosing between fixed and variable-rate loans. Locking in a fixed rate could be advantageous when rates are expected to decline, while variable rates may be suitable for short-term financing in a tightening cycle.
Long-Term Economic Consequences
Persistent high interest rates can dampen economic activity by discouraging borrowing. This can lead to reduced consumer spending, delayed corporate expansion, and even slowed job creation. On the other hand, if rates drop too quickly, excessive credit growth could fuel asset bubbles, as seen in past financial crises. The balancing act for banks and policymakers remains complex.
What Borrowers Should Expect Moving Forward?
Given the current financial landscape, borrowers should stay informed on central bank decisions and macroeconomic indicators. Fixed-rate loans may become more attractive in markets where rate cuts are anticipated, while variable-rate loans remain a viable option in economies where inflation remains a concern.
Stay Updated with Us
We will continue monitoring global interest rate trends and their impact on loan rate-type offers. Stay with us for expert analyses, financial insights, and strategic borrowing advice.
How do you see interest rate trends influencing your financial decisions? Share your thoughts below, and check back daily for the latest updates on this evolving topic.







equilibrado dinámico
Aparatos de ajuste: importante para el rendimiento uniforme y efectivo de las equipos.
En el mundo de la ciencia avanzada, donde la rendimiento y la estabilidad del equipo son de suma significancia, los dispositivos de ajuste tienen un función fundamental. Estos aparatos adaptados están concebidos para balancear y fijar partes móviles, ya sea en dispositivos productiva, automóviles de traslado o incluso en dispositivos caseros.
Para los expertos en mantenimiento de dispositivos y los ingenieros, trabajar con dispositivos de calibración es fundamental para asegurar el operación uniforme y fiable de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas alternativas avanzadas sofisticadas, es posible reducir sustancialmente las sacudidas, el ruido y la tensión sobre los cojinetes, mejorando la longevidad de partes caros.
También trascendental es el tarea que tienen los sistemas de equilibrado en la servicio al cliente. El apoyo experto y el mantenimiento permanente utilizando estos sistemas facilitan proporcionar prestaciones de óptima excelencia, mejorando la satisfacción de los consumidores.
Para los dueños de negocios, la financiamiento en unidades de balanceo y detectores puede ser fundamental para mejorar la efectividad y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente significativo para los inversores que administran medianas y medianas empresas, donde cada elemento es relevante.
Además, los dispositivos de equilibrado tienen una gran implementación en el sector de la prevención y el monitoreo de calidad. Habilitan encontrar posibles defectos, evitando arreglos costosas y perjuicios a los equipos. Incluso, los resultados generados de estos dispositivos pueden usarse para optimizar procesos y mejorar la exposición en plataformas de consulta.
Las campos de uso de los dispositivos de balanceo cubren diversas sectores, desde la elaboración de vehículos de dos ruedas hasta el supervisión de la naturaleza. No importa si se considera de grandes fabricaciones industriales o modestos espacios caseros, los equipos de ajuste son esenciales para proteger un rendimiento eficiente y sin paradas.